- Nephron: The functioning part of the kidney, it does the filtration and the controlling of the composition of the blood.
- Bowman's capsule: The dead end to the Nephron.
- Proximal Convoluted tubule: The first twisted section.
- Distal Convoluted tubule: The second twisted section.
- Glomerulus: Filters the blood and is surrounded by the bowman's capsule
- Loop of Henle: Leads the Proximal tubule to the distal tubule there are millions of Nephrons in the kidney.
Sunday, November 6, 2011
2.70 Nephron Structure
2.71 Ultrafiltration
- The blood arrives in the kidney through the Afferent Arteriole.
- The Arteriole begins to branch off and create a twisted knot-like structure called the Glomerulus.
- The diameter of the Efferent Arteriole is smaller.
- This creates a high pressure.
- Plasma which is salts, water, amino acids, urea and glucose is forced out of the blood vessel and into the inside of Bowman's capsule.
- This is called the Glomerular filtrate.
Saturday, November 5, 2011
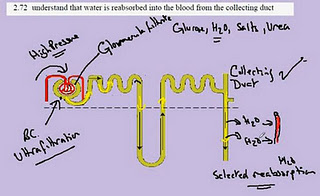
2.72 Water re-absorbtion
- When the ultrafiltration occurs in the Bowman's capsule, too much water is filtered.
- The water is removed from the filtrate.
- It is then added into the blood vessels.
- This is called selective reabsorption.
- As it passes through the Collecting Duct, water is removed from the filtrate.
2.73 Glucose re-absorption
- A molecule is selected and is reabsorbed back into the blood.
- The molecule gets removed from the blood and is put back in.
- If there is glucose in urine, the person could have diabetes.
- There usually is no glucose in urine.
- In the first convoluted tubule glucose is removed and out back into the blood.
2.74 ADH
- ADH- Anti Diuretic Hormone.
- ADH increases the permeability of the kidneys which allows them to re-absorb more water.
- It flows through the blood stream to the kidneys.
- It is produced in the region of the brain known as the hypothalamus.
- It controls the amount of water in the blood.
- Tissue fluid should be isotonic with the cells.
2.75 Urine
- Urine contains water salts and urea.
- The removal of urea is a part of excretion and metabolic waste.
- Salts and urea is removed by osmoregulation to maintain isotonic tissue.
- The salt, water and urea composition in each person varies depending on the condition the person is in.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)