- Nephron: The functioning part of the kidney, it does the filtration and the controlling of the composition of the blood.
- Bowman's capsule: The dead end to the Nephron.
- Proximal Convoluted tubule: The first twisted section.
- Distal Convoluted tubule: The second twisted section.
- Glomerulus: Filters the blood and is surrounded by the bowman's capsule
- Loop of Henle: Leads the Proximal tubule to the distal tubule there are millions of Nephrons in the kidney.
Sunday, November 6, 2011
2.70 Nephron Structure
2.71 Ultrafiltration
- The blood arrives in the kidney through the Afferent Arteriole.
- The Arteriole begins to branch off and create a twisted knot-like structure called the Glomerulus.
- The diameter of the Efferent Arteriole is smaller.
- This creates a high pressure.
- Plasma which is salts, water, amino acids, urea and glucose is forced out of the blood vessel and into the inside of Bowman's capsule.
- This is called the Glomerular filtrate.
Saturday, November 5, 2011
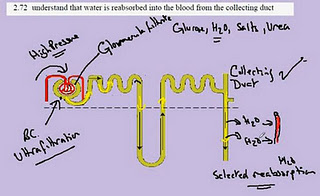
2.72 Water re-absorbtion
- When the ultrafiltration occurs in the Bowman's capsule, too much water is filtered.
- The water is removed from the filtrate.
- It is then added into the blood vessels.
- This is called selective reabsorption.
- As it passes through the Collecting Duct, water is removed from the filtrate.
2.73 Glucose re-absorption
- A molecule is selected and is reabsorbed back into the blood.
- The molecule gets removed from the blood and is put back in.
- If there is glucose in urine, the person could have diabetes.
- There usually is no glucose in urine.
- In the first convoluted tubule glucose is removed and out back into the blood.
2.74 ADH
- ADH- Anti Diuretic Hormone.
- ADH increases the permeability of the kidneys which allows them to re-absorb more water.
- It flows through the blood stream to the kidneys.
- It is produced in the region of the brain known as the hypothalamus.
- It controls the amount of water in the blood.
- Tissue fluid should be isotonic with the cells.
2.75 Urine
- Urine contains water salts and urea.
- The removal of urea is a part of excretion and metabolic waste.
- Salts and urea is removed by osmoregulation to maintain isotonic tissue.
- The salt, water and urea composition in each person varies depending on the condition the person is in.
Sunday, October 30, 2011
2.69 Urinary system
- There are two kidneys in the urinary system with separate blood supplies, they carry out filtration, excretion and Osmoregulation.
- The kidneys use the process of excretion and filtration.
- Each kidney there is a tube which lead to the bladder called the ureter.
- The ureter carries urine from the kidney to the bladder.
- The urine is conducted to the outside of the body down the urethra, to be excreted which travels down the vagina or penis.
2.68b Osmoregulation
- Osmoregulation means control of Osmosis.
- Tissue fluid, surrounding the cells in the body are isotonic with the cytoplasm of the cells.
- It means that the amount of water going in and out of these cells are equal, and the cells will stay the same size and maintain their function.
- The danger of the tissue is that blood circulating into the tissue is concentrated, causing a hypertonic tissue fluid.
- It also may be very dilute causing a hypotonic tissue fluid.
2.68a Excretion
- The urea contains nitrogen which is toxic to the body and cannot be stored.
- The original form of nitrogen are amino acids.
- Blood circulates into the liver and breaks down, and it is converted into Urea.
- It re-enters the blood stream and circulates to both kidneys.
- The kidneys filter the urea from the blood and will be added to water to form urine.
2.67b Human organs of Excretion
- The lungs excrete carbon dioxide through respiration.
- The kidneys excrete H20, Urea and Salts.
- Skin excretes water and salt through the process of sweating and also abit of Urea.
2.67a Excretion in plants
- Photosynthesis happens when a leaf absorbs light energy and in this process it combines CO2 with water to form glucose and oxygen which are given off as waste molecules.
- CO2 + H2O ---> C6H12oO6 + O2 -> Excretion
- Glucose and Oxygen happen through enzyme reactions, the glucose is broken down and forms ATP.
- Carbon dioxide is a metabolic waste and is excreted.
- C6H12oO6 + O2 ---> ATP + H2O + H2O -> Respiration
- Glucose molecule are broken down and energy is used to form ATP and get the waste of carbon dioxide and water to be given off.
- This waste process is called Excretion.
Saturday, October 1, 2011
Saturday, September 24, 2011
Sunday, September 18, 2011
3.2 Fertilisation
- The adult male and female gametes are formed by meiosis.
- When we have sufficient cells this will then be called an embryo.
- The cells that are formed by meiosis have half as many chromosomes as the cell that formed them.
- Fertilisation occurs when a male and female gamete join.
- The zygote divides into a ball of cells, called the blastula which then grows to form the embryo.
Sunday, September 11, 2011
3.9a Male reproduction system
- Urine is stored in the bladder.
- The penis carries the sperm into the vagina.
- Sperm is stored in the epididymis.
- The seminal vesticle produces 70% of the semen.
- Urethra is the tube which connects the testes and the SV which takes semen to the penis.
Thursday, September 8, 2011
3.12 Amniotic Fluid
- Amniotic fluid is found inside the embryo.
- If anything happens to the outside uterus amniotic fluid prevent anything happening to the unborn child.
- Amniotic fluid can't be compressed, it absorbs pressure.
Sunday, September 4, 2011
3.11 Placenta
- The placenta grows out of the developing embryo not the mother.
- The blood vessels inside the placenta are the child's blood vessels including arteries and veins.
- The placenta grows into the wall of the uterus.
- Glucose, amino acids and fats travels through the mother's blood stream and into the wall of the uterus.
- Glucose, amino acids and fats will cross into the child's blood at the placenta.
- Amino acids, sugars and fats will go from the mother's to the child's blood.
Sunday, August 28, 2011
3.24a Mitosis
- Mitosis is a type of cell division that leads to growth and repair.
- The amount of chromosomes in a nucleus is called the diploid numbers.
- When a cell is divided by mitosis each cell is identical and two new cells are formed.
- Growth occurs by increase in the number of cells.
- All humans have 46 (2n) amount of chromosomes.
3.24b Mitosis
- Chromosomes make identical copies of themselves.
- Two daughter cells form with the identical chromosomes and the parent cells.
- When this happens it is DNA replication.
- What hold the DNA together is something called the centromere which is located in the middle of the chromosome.
- When this occurs they are know as a pair of chromotids.
3.24c Mitosis
- When a cell first breaks down it shows that it is entering the process of mitosis and cell division.
- Chromosomes become visible as "chromotids" in a pair after the breakdown of the membrane.
- As cell division carries on fibres form and each end of the cells.
- Chromotids line up in the middle of the cell and are pulled apart by fibres.
- The nucleus forms around the chromosomes at each end causing two nuclies.
Sunday, August 21, 2011
3.16 DNA and Genetic information
- One chromosome contains thousands of genes.
- There are 4 kinds of bases called: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine.
- They are found in DNA in the pairs: Thymine-Adenine and Guanine-Cytosine.
- When you magnify one gene you can see a double helix which appear parallel.
- Genes contain an organized structure of bases in this order: ATCGAACCAG.
Question: Why do double helix's appear in parallel shape?
3.15 Genes
- Genes are located in the nucleus.
- A double helix shaped gene carries information of the characteristic of the organism.
- Information of the gene is passed to the cytoplasm.
- After passing into the cytoplasm the gene is then turned into a protein.
- Protein controls the characteristic of the gene.
Question: Does that amount of genes you have change your gender?
3.14 Chromosomes
- A chromosome is the genetic information inside a cell.
- Genes control the production of protein which controls a characteristic.
- Chromosomes have a DNA that forms a shape which is called a double helix.
- Each different species have different amount of chromosomes.
- Chromosomes operate in pairs which are based on length.
Question: What is the organized structure of a chromosome?
Thursday, August 18, 2011
3.1 Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
- Organisms that have sexual reproduction show sexes that is when they can be identified as a male or female.
- There are tho different type of genders which are males and females.
- Males have sperm and females have eggs.
- Fertilization is the process of fertilizing an egg of a female animal or a plant involving the fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
- All humans are different, physically and mentally and don't look alike unless they are un identical twins.
Sunday, June 19, 2011
4.9 Carbon Cycle
- C02+H20 are combined in photosynthesis using light energy.
- Light energy is trapped and used to form organic molecules such as glucose.
- The C02 comes from the atmosphere which makes 0.03% of the atmosphere.
- Photosynthesis is responsible for reducing the atmospheric C02.
- The passage of carbon through the various trophic level we have identified the producer but then producers are eaten by primary consumers.
- The primary consumer takes in the carbon from the producer and uses it to reconstitute body materials so it grows.
Tuesday, June 14, 2011
My First Post
Replace the subject line and body with your first post and hit send! Include pictures, an mp3, or anything else you want to share. It's just that simple.
Sunday, June 12, 2011
4.14 Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
- Water Vapor, Methane and Carbon dioxide are all greenhouse gases.
- Greenhouse gases changes the climate.
- The UV rays are increasingly re-emitted which warms the earth's surface.
- Melting ice case, raising sea levels can happen due to Greenhouse gases.
4.13 Greenhouse Gases
- Burning of fossil fuels - N02, C02, S02.
- Evaporation of water.
- Canned spray - Deodorant, Room freshener.
4.12 Greenhouse Effect
- UV light comes from the sun.
- UV light is converted as infrared and absorbed.
- 50% of UV light is reflected.
- The more the greenhouse gases the more heat there is.
- Infrared gets emitted back out.
4.11 Gas Pollution
- The burning of fossil fuels results in sulphur dioxide gas.
- Sulphur dioxide happens mostly because of factories and cars.
- Acid rain kills fish in lakes and rivers.
- Carbon monoxide blocks hemoglobin which can lead to death.
- S02+H20 -Sulphuric acid - Acid rain.
Tuesday, May 17, 2011
Sunday, May 15, 2011
4.7 Energy Efficiency
- Losses in the owl is from respiration, producing energy for flight, digestion, movement, the nervous system.
- All organisms finally die and are broken down by micro-organisms living on the dead and decaying remains of other micro-organisms.
- 100Kj of grass energy represents grass eaten by the herbivore.
- Mouse have to walk around and find their food and carry out the process of respiration.
- 90Kj of energy left is lost from respiration and undigested food.
4.6 Energy and substances in food chains
- Bush grass is eaten by impala.
- Bush grass is the producer Impala is the primary consumer leopard is the secondary
- consumer.
- Producer turns light energy into chemical energy - takes the form of organic molecules including carbohydrates, proteins and lipids --> what we call food.
- These molecules are composed of C-H bonds, C-O bonds, C-C bonds, O-H bonds and C-N bonds - ALL represent energy.
4.5b Food Webs
- Food webs allow better description of the ecosystem.
- Food web allows us to show organisms feeding at different trophic levels.
- Organisms can have multiple predators.
- Organisms may be feeding on multiple pray.
- Results in food chains becoming linked.
4.5a Food Chains
- Food in China links together producer to the 1st consumer, 2nd consumer and 3rd consumer.
- Only one organism per trophic level.
- Food chain cannot show an organism being an omnivore.
- Cannot show them feed at more than 2 trophic levels.
- Food chains show the flow of matter and energy.
4.4 Trophic Levels
- Trophic means to feed.
- Carrot plant>Photosynthesis>Producer.
- Producer turns light energy into chemical energy.
- Primary Consumer takes in the chemical energy of the plant and changes it into chemical energy of the fly.
- All organisms die and are then broken down by decomposers of fungi and bacteria.
Sunday, May 8, 2011
4.3 Quadrates samples
- The sample needs to be random (bias).
- The second part of the sample is that it needs to be representative (large).
- A sample needs to be big enough so the estimate has to be close to the real population.
- The grid system is going to work like the x,y coordinates on a graph you would draw.
- The random numbers are used to generate a number for the x and y coordinates and will tell us where to take a sample from.
4.2 Quadrates
- Quadrates are used to estimate the population size of an organism in two different areas.
- All ecosystems are made up of a number of populations which formed the community.
- The technique is called quadrating, it is based on squares and can be made from an material.
- They form square grids which can consist of 0.25 meter or 1 meter.
- Quadrates are a method of sampling different locations so populations can be compared in two different locations.
4.1 Ecosystems
- A community of organisms consist of a population of different species.
- The habitat includes the non biological factors.
- The environment could have the cycle of daylight with dark, the temperature, rainfall, humidity and slope of the land.
- All the factors have something in common; they are all non biological.
- The community which is made up from different species interact with each other.
Sunday, April 24, 2011
3.4 Plant Fertilization
- The pollen tubes will only complete if they are from the same species.
- The nucleus travels down the pollen tube and into the ovule.
- Pollen nucleus will fertilize the ovule and will leave to a formation of a zygote and will grow into the embryonic plant.
- The outside of the ovule forms the seed coat also know as the TESTA.
- Cotyledons are the food stores for the seedling and will support the plant until it develops its first set of leaves.
Sunday, April 3, 2011
3.3 a Insect pollination
- A pollination flower transfers pollen grain from the anther to a stigma of a plant.
- A pollen is a small structure that contains male nuclei.
- Transfer in an insects pollinated plant is taken place by insects.
- Its necessary for this plant to attract insects.
- If pollen goes from one plant to another this is called cross pollination.
3.3 b Wind pollination
- Transfer of the pollen grains are from the anther.
- The pollen grain from the anther to the stigma is through air carried by the wind.
- Pollen grain has lightweight pollen grains, which some wing feature.
- It would probably let it move for efficiently through the air.
- There is no color in the petals and no smell to attract insects.
Sunday, March 27, 2011
2.81 Phototropism
- The word phototropism means light growth, suggesting that the growth is towards the light.
- The light comes in all directions meaning that the light will grow forward.
- If light comes into the plant sideways that means that the plant will grow in the direction the light is coming in.
- The light on one side causes the plant to move to the opposite side.
- Auxin causes more growth to the plant which makes the plant grow in the other direction an also causes the plant to bend.
- Cell division is called mitosis which means that the cells multiply.
Friday, March 25, 2011
2.80 Geotropism
- Geo of Geotropism stands for gravity and tropism stands for growth response.
- The embryonic roots grown downwards and it's called positive geotropism.
- Where the embryonic roots grow upwards it is negative geotropism.
- Plants commonly exist in a state of "anisotropic growth," where roots grow downward and shoots grow upward.
- No matter what you do to a plant within Earth's atmosphere, it will still grow roots down, stem up.
2.79 Plants and Stimuli
- Stimuli is the changes in the environment such as temperature or light changes.
- The plant has receptors that can detect stimuli and turn that into a response, usually the responses make them grow called tropism.
- Tropism involves light is called phototropism, gravity, geotropism.
- The connection between the receptors and response usually take to place plant hormones, such as auxin.
- Auxins are a class of plant growth substances its role in the plant is usually structure and growth.
Thursday, March 24, 2011
2.55 Rate of transpiration
- Transpiration is the loss of water through a leaf.
- Absorption of sunlight through the leaf transforms water into heat.
- For evaporation to happen the liquid has to turn into a gas through diffusion through the stomatal pore.
- The concentration gradient for water if there is a big difference there would be a high rate of transpiration.
- If the humidity was low that would make the rate of transpiration slow, with high temperature you would get more evaporation.
Monday, March 21, 2011
2.17 Photosynthesis
- The source of light energy is the sun.
- The plants need carbon hydrogen, and oxygen through the stems.
- The water molecules come out at the xylem into the palisade layer.
- Photosynthesis occurs in the palisade layer.
- The phloem stores the minerals and food.
Sunday, March 20, 2011
2.53 Uptake of Water
- Water is collected from the roots of the plants and travels up the stem.
- The root has a big surface area so the root can absorb a lot of water.
- Water enters through the epidermis of the roots.
- Even though there is no water, minerals enter freely.
- In the plant through osmosis water moves from a dilute to a concentrated region.
2.54 Transportation
- For water to turn into gas it requires heat.
- Heat is supplied by sunlight as it is absorbed by the plant structure.
- Evaporation happens through the stomatal pore.
- Water is delivered into the leaf by the xylem.
- Water vapor diffuses down the diffusion gradient and through the stomatole pore.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)